1D:Dialog SurfaceTransferCoefficients: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| Zeile 16: | Zeile 16: | ||
* The <B>"Heat Resistance [m²K/W]"</B> (the reciprocal of the [[Details:HeatTransfer | heat transfer coefficient]] [W/m²K]),<BR> which governs the convective and (long-wave) radiative heat exchange between the component and the surroundings.<br> <BR> You can select between a constant coefficient (which is sufficient for most cases) and a wind-dependent coefficient.<br> <BR> If you have activated the option <B>"wind-dependent"</B>, WUFI determines the heat transfer coefficient as follows, in dependence of the format of the selected [[Details:Climate | climate file]]:<br> <BR> | * The <B>"Heat Resistance [m²K/W]"</B> (the reciprocal of the [[Details:HeatTransfer | heat transfer coefficient]] [W/m²K]),<BR> which governs the convective and (long-wave) radiative heat exchange between the component and the surroundings.<br> <BR> You can select between a constant coefficient (which is sufficient for most cases) and a wind-dependent coefficient.<br> <BR> If you have activated the option <B>"wind-dependent"</B>, WUFI determines the heat transfer coefficient as follows, in dependence of the format of the selected [[Details:Climate | climate file]]:<br> <BR> | ||
** <B>[[Details:TRY-File | TRY]] and [[Details:IWC-File | IWC]] format:</B><br> If the [[1D:Dialog_Orientation | inclination]] of the component is greater than 10° and the surface of the component is [[1D:Dialog_Orientation | facing away]] from the mean wind direction (i.e. leeward conditions):<br> & | ** <B>[[Details:TRY-File | TRY]] and [[Details:IWC-File | IWC]] format:</B><br> If the [[1D:Dialog_Orientation | inclination]] of the component is greater than 10° and the surface of the component is [[1D:Dialog_Orientation | facing away]] from the mean wind direction (i.e. leeward conditions):<br />α = 0.33 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5 [W/m²K].<br> <BR> Else (windward conditions):<br> α = 1.6 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5 [W/m²K].<br> <BR> 4.5 W/m²K is the convective heat transfer coefficient for v_wind = 0 m/s and 6.5 W/m²K ist the radiative component.<BR> <BR> | ||
** <B>[[Details:DAT-File | DAT]] format:</B><br> Same method as with TRY, but DAT files may also indicate variable wind (wind direction "999"). In this case, the average of leeward and windward conditions is used.<br> <BR> | ** <B>[[Details:DAT-File | DAT]] format:</B><br> Same method as with TRY, but DAT files may also indicate variable wind (wind direction "999"). In this case, the average of leeward and windward conditions is used.<br> <BR> | ||
** <B>[[Details:WET-File | WET]] format:</B><br> Instead of a general mean wind direction, the WET format offers detailed information about the frequency of different wind directions during the hourly measurement interval.<br> <BR> If the [[1D:Dialog_Orientation | inclination]] of the component is less than 10° (i.e. permanent windward conditions):<br> <BR> <FONT FACE="SYMBOL">a</FONT> = 1.6 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5 [W/m²K].<br> <BR> Else:<br> <FONT FACE="SYMBOL">a</FONT> = weight_windward * (1.6 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5) + weight_leeward * (0.33 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5) [W/m²K].<br> <BR> The weighting factor weight_windward is the sum of the components of the measured wind directions perpendicular to the component surface and weighted according to their duration.<BR> <BR> Weight_leeward is (1 - weight_windward).<BR> <BR> 4.5 W/m²K is the convective heat transfer coefficient for v_wind = 0 m/s and 6.5 W/m²K ist the radiative component.<BR> <BR> | ** <B>[[Details:WET-File | WET]] format:</B><br> Instead of a general mean wind direction, the WET format offers detailed information about the frequency of different wind directions during the hourly measurement interval.<br> <BR> If the [[1D:Dialog_Orientation | inclination]] of the component is less than 10° (i.e. permanent windward conditions):<br> <BR> <FONT FACE="SYMBOL">a</FONT> = 1.6 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5 [W/m²K].<br> <BR> Else:<br> <FONT FACE="SYMBOL">a</FONT> = weight_windward * (1.6 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5) + weight_leeward * (0.33 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5) [W/m²K].<br> <BR> The weighting factor weight_windward is the sum of the components of the measured wind directions perpendicular to the component surface and weighted according to their duration.<BR> <BR> Weight_leeward is (1 - weight_windward).<BR> <BR> 4.5 W/m²K is the convective heat transfer coefficient for v_wind = 0 m/s and 6.5 W/m²K ist the radiative component.<BR> <BR> | ||
Version vom 23. März 2009, 10:57 Uhr
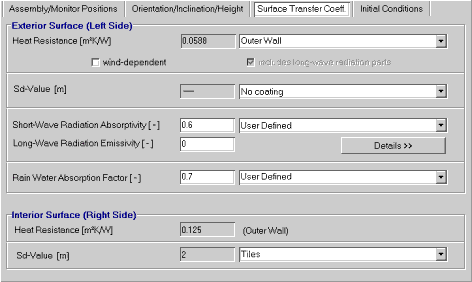
Dialog: Surface Transfer Coefficients
The surface transfer coefficients indicate to which extent the conditions in the surroundings affect the building component, especially the heat and moisture flows through its surfaces.
WUFI uses the following surface transfer coefficients:
"Exterior surface":
- The "Heat Resistance [m²K/W]" (the reciprocal of the heat transfer coefficient [W/m²K]),
which governs the convective and (long-wave) radiative heat exchange between the component and the surroundings.
You can select between a constant coefficient (which is sufficient for most cases) and a wind-dependent coefficient.
If you have activated the option "wind-dependent", WUFI determines the heat transfer coefficient as follows, in dependence of the format of the selected climate file:
- TRY and IWC format:
If the inclination of the component is greater than 10° and the surface of the component is facing away from the mean wind direction (i.e. leeward conditions):
α = 0.33 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5 [W/m²K].
Else (windward conditions):
α = 1.6 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5 [W/m²K].
4.5 W/m²K is the convective heat transfer coefficient for v_wind = 0 m/s and 6.5 W/m²K ist the radiative component.
- DAT format:
Same method as with TRY, but DAT files may also indicate variable wind (wind direction "999"). In this case, the average of leeward and windward conditions is used.
- WET format:
Instead of a general mean wind direction, the WET format offers detailed information about the frequency of different wind directions during the hourly measurement interval.
If the inclination of the component is less than 10° (i.e. permanent windward conditions):
a = 1.6 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5 [W/m²K].
Else:
a = weight_windward * (1.6 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5) + weight_leeward * (0.33 * v_wind + 4.5 + 6.5) [W/m²K].
The weighting factor weight_windward is the sum of the components of the measured wind directions perpendicular to the component surface and weighted according to their duration.
Weight_leeward is (1 - weight_windward).
4.5 W/m²K is the convective heat transfer coefficient for v_wind = 0 m/s and 6.5 W/m²K ist the radiative component.
- WAC and WBC Format:
Same method as with TRY if the file contains wind direction and wind speed (scalar or vectorial). Otherwise, no wind-dependent heat transfer coefficient can be determined, and WUFI simply uses the value in the text box.
- KLI format:
This format does not contain any information about wind speed or direction, so that no wind-dependent heat transfer coefficient can be determined, and WUFI simply uses the value in the text box.
- TRY and IWC format:
The heat transfer resistance is the reciprocal of the heat transfer coefficients determined in these ways.
Note: the resulting values of the heat resistance over time can be output as an ASCII export or as a curve in the result graphs. This allows you to access the values determined by WUFI.
"includes long-wave radiation part":
With this checkbox you can tell WUFI whether the user-defined heat resistance
you entered contains a component due to long-wave radiation
or not. All the predefined values in the drop-down list contain such a component.
This option becomes relevant if you want to do a computation with full long-wave
radiation balance (otherwise, it is not enabled). For details please refer to the help
topic Long-Wave Radiation Exchange.
- The "Sd-value [m]",
of a surface 'coating' (if present), such as a paint coat, wallpaper, vapor retarder, weathered surface zone etc. This allows to account for the diffusion-retarding effect of such a 'coating' without the need to explicitly include the possibly very thin layer in the component assembly.
If there is no such coating on your building component, or any coating has been included in the assembly as a separate layer, select "No coating".
The normal water vapour transfer resistance which is due to the boundary air layer is always automatically allowed for by WUFI and need not be included in the sd-value.
Please refer to reference: Surface Coatings for further details on the use of this option.
- The "Short-Wave Radiation Absorptivity [-]",
which determines the fraction of total incident (short-wave) solar radiation that is absorbed by the component.
- The "Long-Wave Radiation Emissivity [-]",
which describes the efficiency of long-wave emission (heat loss by thermal radiation).
In building physics, the long-wave radiation exchange between the component and its surroundings is usually accounted for by appropriately increasing the heat transfer coefficient. This is accurate enough for most applications, only details like nighttime radiative cooling and subsequent dew deposition and mold growth risk cannot be handled this way.
If you can do without nighttime cooling, we recommend to set the long-wave emissivity to zero.
Otherwise, enter the emissivity of the component's surface. But then you must make sure that WUFI is working in the appropriate calculation mode and that you are using appropriate weather data (including, in particular, data on the long-wave radiation exchange). For details, see the topic Long-wave Radiation Exchange. Because of the relatively large amounts of energy involved in the long-wave exchange, insufficient attention to these details may produce very inaccurate results.
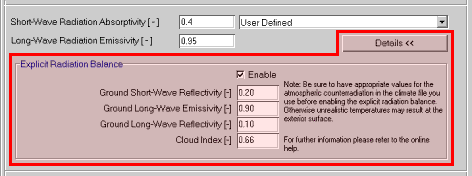
If you want WUFI to work in the calculation mode with explicit radiation balance, you can enable this mode here and set some parameters:
"Ground Short-Wave Reflectivity": gives the fraction of short-wave
global radiation reflected by the terrestrial surroundings. Needed for the radiation
conversion for inclined surfaces.
"Ground Long-Wave emissivity": gives the effective emissivity of
the terrestrial surroundings. Needed for computing the thermal emission of the
surroundings.
"Ground Long-Wave Reflectivity": gives the effective reflectivity of
the terrestrial surroundings. Needed for computing the fraction of atmospheric
counterradiation which is reflected by the surroundings.
"Cloud index": gives the fraction of sky which is covered with
clouds. Allows estimating the atmospheric counterradiation if no measured data are
available.
For further details on these parameters, please refer to the
topic Long-Wave Radiation Exchange.
- The "Rain Reduction Factor [-]",
which takes into account that some of the rain water hitting the wall surface splashes off on impact and is not available for capillary absorption. For ordinary walls, WUFI uses a value of 0.7, which is adequate for most cases. You may select "No absorption", however, if the facade is protected from rain and no rain absorption shall take place at all.
"Interior Surface":
- The "Heat Resistance [m²K/W]" (the reciprocal of the heat transfer coefficient[W/m²K]),
which governs the convective and (long-wave) radiative heat exchange between the component and the surroundings.
- The "Sd-value [m]",
of a surface 'coating' (if present), such as a paint coat, wallpaper, vapor retarder, weathered surface zone etc. This allows to account for the diffusion-retarding effect of such a 'coating' without the need to explicitly include the possibly very thin layer in the component assembly.
If there is no such coating on your building component, or any coating has been included in the assembly as a separate layer, select "No coating".
The normal [Details:WaterVaporTransfer | water vapour transfer resistance]] which is due to the boundary air layer is always automatically allowed for by WUFI and need not be included in the sd-value.
Please refer to reference: Surface Coatings for further details on the use of this option.
For all of these coefficients WUFI offers you predefined values which you can select from
a drop-down list. You may enter user-defined values as well.
The type of building element selected for the exterior heat resistance also determines
the interior heat resistance and the rain reduction factor.
Version notice: user-defined values can be entered in WUFI Pro
only.
The use of the heat resistance instead of the heat transfer coefficient reflects recent changes of nomenclature in relevant standards.